Private investigator
Hacker team “Fancy Bear” aged Google’s Accelerated Cell Pages to lift Gmail passwords
Published
 Shutterstock)” decoding=”async” fetchpriority=”high” >
Shutterstock)” decoding=”async” fetchpriority=”high” >
A hacking team reportedly linked to the Russian government has been the utilization of a security flaw in a Google carrier to open attacks on investigative journalists. The earn huge knew about the vulnerability and took some measures to repair it but without disclosing what they were so that they’re most regularly subjected to glance-overview.
The safety malicious program lies within Google’s implementation of a brand new cyber web weird and wonderful it has been attempting to promote known as Accelerated Cell Pages (AMP). Google has marketed AMP as a strategy of optimizing on-line pages for smartphones. Launched in slack 2015, AMP is designed to provide more sparkling versions of websites that might presumably load sooner on the on the complete slower knowledge connections and microprocessors aged by cell units.
To extra breeze issues up for smartphone users, Google preloads copies of AMP pages listed in search outcomes to allow them to even fair additionally be at as soon as loaded if they’re attributable to this truth clicked. The one technique this background loading of pages might presumably fair additionally be carried out is to give the cached pages Google.com URLs.
Such pre-rendered AMP pages created by Google demonstrate the originating arena on the tip of the webpage tell material residence. But within a cell web browser’s address bar — on the very top of the show cloak cloak — they nonetheless appear to be from Google’s web effect of dwelling. Furthermore, the disclaimer showing the effect the earn page in fact originates will proceed as the particular person scrolls down the earn page, whereas the Google address is no longer going to. This assemble might presumably fair additionally be viewed within the video below.
Thanks to heavy promotional efforts by Google, AMP has been broadly adopted. But it absolutely has additionally remained controversial within the on-line publishing industry. Essentially, its critics have confidence raised concerns that AMP pages obfuscate lawful URLs, limit the interface that web sites can contemporary to their readers, and back searchers to never hobble away the Google effect of dwelling.
“Why would any web effect of dwelling turn their complete cell viewers — a majority portion of their complete viewers, for many web sites this day — over to Google?” effectively-identified blogger and programmer John Gruber wrote rapidly after AMP changed into unveiled.
Diversified technical-minded critics of AMP have confidence seen its possible for abuse by junk web sites. Since AMP webpages might presumably fair additionally be accessed by job of Google addresses, they appear more credible than random domains or weblog cyber web cyber web hosting web sites admire WordPress.
In December, tech journalist Kyle Chayka additionally illustrious that AMP and Facebook’s competing “Immediate Articles” characteristic allow junk web sites that publish nonsense or conspiracy theories to portion many of the identical visible capabilities as legitimate data web sites. “All publishers pause up attempting more identical than diversified. That makes environment apart the accurate from the fallacious even more challenging.”
“Google AMP is inappropriate data for how the on-line is built, it’s inappropriate data for publishers of credible on-line tell material, and it’s inappropriate data for consumers of that tell material,” computer guide author Scott Gilbertson wrote earlier this year in an essay titled “Raze Google AMP forward of it KILLS the on-line.”
Previous its possible for abuse by dishonest web publishers, Google’s technique to caching AMP webpages and offering Google.com addresses for them is a top target for cyber-criminals who lift chronicle knowledge the utilization of a technique identified as phishing. Most computer users have confidence encountered this one day: Incorrect security indicators designed to glance admire messages from legitimate firms, spirited targets to keep in touch over with plausible-attempting web sites effect of dwelling up fully for the reason of capturing passwords.
Since phishing has change into rather more current, community administrators have confidence made a addiction of telling users never to click on password reset links that hobble to diversified domains. Due to this of the technique that Google has implemented AMP, on the choice hand, Gmail users and folks the utilization of Google apps for institutional utilize are in fact more inclined to such attacks. Phishers who utilize AMP pages can thereby utilize reliable “google.com” web addresses to bid users to malicious web sites.
“It is miles a considerable malicious program personally,” web programmer Ray Etornam wrote to Google, in a file he filed closing November on the applying pattern effect of dwelling Github discussing how fallacious data publishers can utilize AMP to intention legitimacy. Commenting on the file that Etornam had submitted, one other developer named Christian Gloddy over and over tried to warn Google about the protection implications of its AMP implementation.
“The most typical suggestion to steer certain of phishing and scams is ‘take a look at the arena within the address bar.’ No longer on the text that might presumably presumably also very effectively be below the address bar,” he wrote in one comment.
A pair of diversified builders underscored that warning to Google even as Malte Ubl, the firm employee accountable for AMP, pushed inspire insistently in opposition to the criticism. “The Google Search viewer clearly attributes the approved arena on the tip,” he wrote. “I don’t agree that an unsophisticated particular person might presumably very effectively be fooled by this.”
Ubl’s defenses were unpersuasive to the builders he changed into attempting to persuade, on the choice hand.
“I judge this scenario is going to chunk Google when least expected and in a in fact public and detrimental technique,” John Pettitt, co-founding father of a credit ranking card cost machine known as CyberSource, wrote within the discussion thread.
* . * . *
While Google changed into busy defending its AMP implementation, hackers affiliated with the cyber-criminal neighborhood most regularly most regularly known as Love Possess, Strontium or APT28 were busy exploiting these very identical flaws to lift a witness at to lift passwords from Gmail users.
Continuously linked with Russian government intelligence operators, Love Possess’s hackers had accrued a legendary status even forward of they were supposed to have confidence participated in a sequence of cyberattacks in opposition to organizations affiliated with the Democratic Celebration closing year. In accordance with Microsoft government vice president Terry Myerson, Love Possess changed into responsible for more viruses the utilization of beforehand unknown vulnerabilities than any diversified hacking confederation.
To this point, many of the oldsters identified to had been pursued by Love Possess by blueprint of a Google AMP exploit appear to had been journalists who were investigating allegations of corruption or diversified wrongdoing by folks affiliated with the Russian government.
One such target changed into Aric Toler, a researcher and author for the on-line effect of dwelling Bellingcat who specializes in examining Russian media and the country’s relationship with a ways-upright groups within Europe and The US. He changed into additionally phase of a Bellingcat investigative team that uncovered proof that Russian-backed rebels had mistakenly shot down Malaysia Airways Flight 17 over Ukraine in 2014, killing all 298 folks on board.
A month forward of critics of Google’s AMP implementation started warning about security vulnerabilities, Love Possess changed into the utilization of them to target Toler in two separate fallacious password-reset messages sent to his interior most chronicle. These messages, which Toler supplied to Salon, utilized an rather more sophisticated murder of password theft known as “spear-phishing,” which combines weird and wonderful phishing ways with insist interior most knowledge gleaned about the target by job of social media and public mailing lists.
On Oct. 12, 2016, Toler bought an electronic mail supposedly from Google alerting him that he had these days modified his security settings to allow older electronic mail programs to uncover entry to his chronicle. “Please be conscious that it is now more straightforward for an attacker to interrupt into your chronicle,” the message warned. It invited him to click on a Google AMP URL redirected to a fallacious webpage designed to capture his electronic mail credentials and transmit them to hackers.
The next day, Toler bought a second message claiming to be from Google alerting him that “government-backed attackers would be attempting to lift your password.” The malicious electronic mail steered him to “Swap password” by clicking on one other Google AMP webpage. The second message appears to had been crafted in step with a tweet Toler had published on Oct. 11 wherein he reported receiving a legitimate electronic mail from Google warning him about “government-backed attackers.”
These messages weren’t sent to Toler at random. They were amongst 14 emails that he bought in 2015 and 2016 attempting to extract his chronicle knowledge out. Significantly, the earlier messages aged a less-sophisticated fallacious link, one created the utilization of the URL shortener Bitly that most fairly web-savvy folks would mark to no longer click. Because the hackers grew more desirous to lift Toler’s knowledge, they aged regularly better ideas.
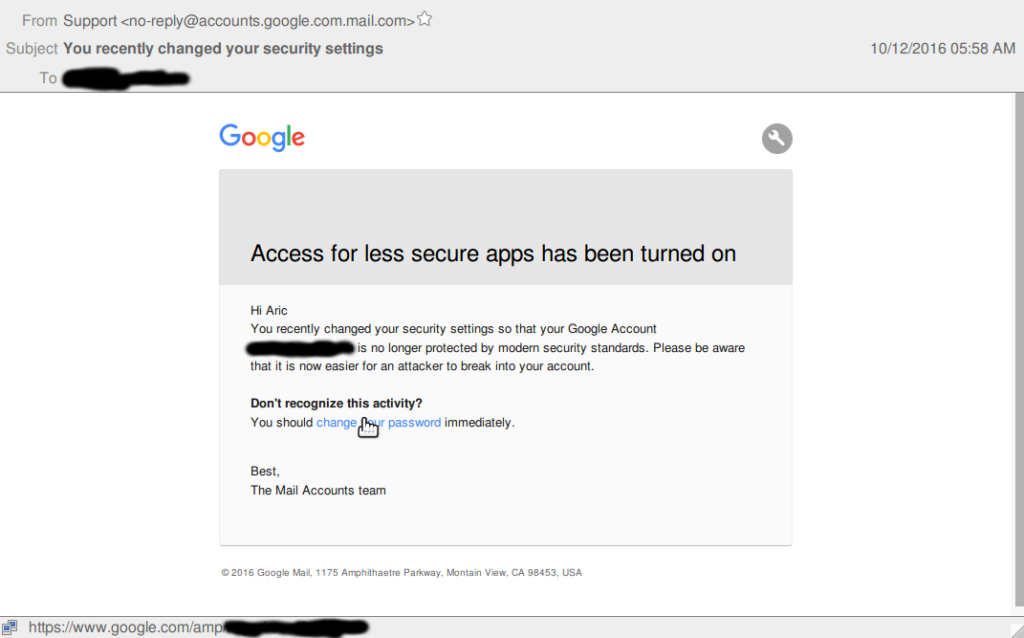 A screenshot of a forged electronic mail from Google that Russian-linked hackers sent to journalist Aric Toler in an strive and lift his chronicle knowledge.
A screenshot of a forged electronic mail from Google that Russian-linked hackers sent to journalist Aric Toler in an strive and lift his chronicle knowledge.
Regardless of their improved technique at exploiting the AMP vulnerability, the hackers who centered Toler bought sloppy. They reused a free electronic mail chronicle registered to annaablony@mail․com that had been had aged in a number of old operations, including making a web site aged in a sure phishing attack that the cybersecurity firm ThreatConnect had archived in its database of identified hacker activities.
“ThreatConnect analyzed the phishing emails Bellingcat bought and diagnosed connections to the Russian threat actor identified as FANCY BEAR/APT 28/Sofacy,” a firm advisor steered Salon. “These emails tried to entice their targets by taking them to a fallacious Google login web page the effect they would enter their credentials. To achieve this, the attackers leveraged each and each Google’s AMP providers and products and link shortening providers and products to obscure the incontrovertible truth that the earn page changed into no longer a legitimate Google effect of dwelling and to murder it glance readable if the target changed into the utilization of a cell phone.”
* . * . *
Toler and his Bellingcat colleagues did no longer fall for Love Possess’s AMP attacks. But one other journalist who writes repeatedly about Russia, David Satter, changed into taken in by a identical AMP phishing message sent by job of the annaablony@mail․com address.
Quickly after Satter changed into tricked into visiting the fallacious web effect of dwelling and coming into his password, a program that changed into cyber web cyber web hosting the positioning logged into his Gmail chronicle and downloaded its complete contents. Inside three weeks, as the Canadian web effect of dwelling Citizen Lab reported, the perpetrators of the hack started posting Satter’s documents on-line, and even altering them to murder opponents and critics of Russian President Vladimir Putin glance inappropriate.
Commenting on Satter’s case in Could fair, John Gruber, the applying developer and early AMP skeptic, wired that even an developed web particular person might presumably very effectively be fooled by a malicious AMP webpage.
“An infinite motive that phishing works is that most folk upright aren’t technically savvy sufficient to give an rationalization for a phony-attempting URL from a legitimate one,” he wrote. “But a URL that in fact is coming from the google.com arena — that’s the murder of link that even a web developer might presumably presumably judge appears to be like legit, especially at a witness.”
While the creator and “tech lead” of Google’s AMP project, Malte Ubl, has been publicly dismissive of external web builders criticizing AMP, the firm says it has “made a preference of changes” to its implementation, even when this might perhaps presumably fair no longer remark what they’re. This tight-lipped habits about its hang insurance policies and habits has made Google infamous within the tech world, even as the firm demands transparency from diversified public actors.
In a assertion forward of this myth changed into published, a Google advisor claimed that AMP links are safe by its “Gain Browsing” technology. The firm did no longer specify when it had implemented this protection, on the choice hand. After this myth changed into published, a Google advisor steered Salon that the Gain Browsing screening of AMP addresses changed into implemented in early January of 2017.
Below the machine, AMP URLs when created by job of a webpage are first visited by a Google security scanner which attempts to envision if they’ve malicious tell material on them.
“Every AMP web page which will additionally be linked to by blueprint of google.com/amp has a minimal of been ‘visited’ by Google’s machine,” a firm advisor steered Salon.
On occasions when Google has no longer pre-screened a webpage, the AMP redirect will give an explanation for a “redirect sight” which informs the person that he/she is being taken to a sure address. The web page additionally gives the users a gamble to attain to the closing effect of dwelling they’d visited “If you happen to attain no longer must always keep in touch over with that web page.”
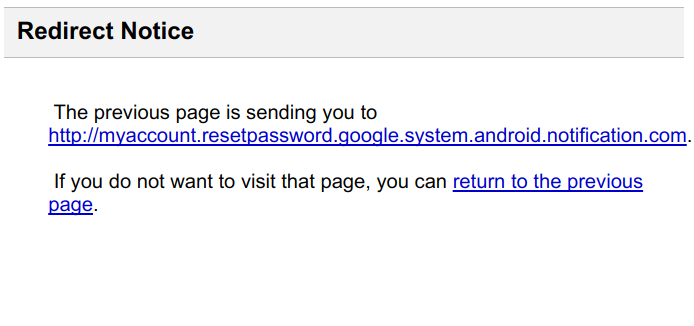
While more purposeful than simply redirecting, the awareness is possible to be unhelpful for computer beginners simply upright attempting to reset their passwords because it’s written in web developer jargon and would no longer remark that clicking the link might presumably presumably doubtlessly be hazardous.
As this text changed into being researched and Salon contacted Google for comment, Ubl blocked public comments on the Github malicious program file filed about Google’s AMP implementation.
At press time, Google is level-headed serving AMP webpages listed in search outcomes from the Google.com arena. One such article from a fallacious data web effect of dwelling claimed that Google changed into itself suppressing proof about the existence of the imaginary planet Nibiru.
“Extra issues … will attain on Google’s aspect within the long term and we’re working with browser distributors to at closing uncover the origin upright,” Ubl wrote in a February update.
Regardless of these assurances, on the choice hand, some folks that work with natty web media firms are beginning to uncover anxious.
“We’ve been supportive of AMP as great as it advantages opponents and leverages the originate web,” Jason Kint, CEO of a web publishing alternate association, steered Salon. Kint’s neighborhood, Digital Reveal Next, counts most U.S.-primarily based fully mostly television networks, the Original York Cases, the Washington Publish, and a range of alternative outstanding web sites as participants.
“This file of an ongoing security scenario is troubling and exactly why consolidation of energy and closed standards are problematic,” Kint mentioned. “The sooner AMP migrates to the originate web and becomes less tied to the pursuits of Google, in every technique the upper.”
This myth has been up thus a ways to consist of knowledge about a partial fix to the AMP security scenario described in this text.
By
Matthew Sheffield
Matthew Sheffield is a national correspondent for The Younger Turks. He is additionally the host of the podcast “Theory of Change.” You might presumably presumably apply him on Twitter.
Private investigator
Associated Topics
——————————————




